Ever wondered how podcasts get that crisp, clear, professional sound? Whether you’re launching your own show, narrating an audiobook, or creating video voiceovers, high-quality audio is essential, and subtle doodle GIF animation touches can make editing easier. You don’t need expensive gear or complex studios—Audacity combined with doodle GIF animation cues can transform your home recordings. With the right techniques, you can polish your voiceovers while experimenting with playful doodle GIF animation visuals, making your audio professional and engaging in 2025.
- What is Audacity, and Why is it Great for Voiceovers & Doodle GIF Animation?
- Why High-Quality Voiceover Recording Matters for Podcasts
- How It Works: Essential Voiceover Recording Tips Using Audacity for Podcasts
- Producing a Podcast Segment in Audacity
- Comparison: Audacity vs. Other Audio Editing Software for Voiceovers
- Common Mistakes to Avoid When Recording Voiceovers in Audacity
- Expert Tips and Best Practices for Audacity Voice Recording
- FAQ Section
- Conclusion
What is Audacity, and Why is it Great for Voiceovers & Doodle GIF Animation?
Audacity is a free, open-source digital audio editor and recording application available for Windows, macOS, Linux, and other Unix-like operating systems. Despite being free, it offers a robust set of features for recording, editing, and processing audio, making it a favorite among podcasters, voiceover artists, and musicians, especially when combined with doodle GIF animation cues. Many users incorporate doodle GIF animation visuals to guide their editing workflow, while subtle doodle GIF animation hints can help make complex processes easier. Audacity also supports integrating playful doodle GIF animation elements, enhancing creativity without complicating audio production.
Why Audacity Stands Out for Voiceovers and Podcasts in 2025:
- Completely Free & Open-Source: This is Audacity’s biggest draw. You get professional-grade recording and editing capabilities without any cost, making it perfect for beginners or those on a budget.
- User-Friendly Interface: While it might look a little dated compared to some paid DAWs, Audacity’s interface is straightforward and easy to navigate. The learning curve for basic recording and editing is relatively gentle, helping you quickly learn Audacity voice editing.
- Powerful Editing Tools: Audacity offers comprehensive tools for cutting, copying, pasting, and deleting audio. You can easily remove mistakes, silence gaps, or rearrange segments of your recording.
- Extensive Effects Library: It comes packed with built-in effects like Noise Reduction, Normalization, Compressor, Equalization, Reverb, and more – all essential for enhancing voiceover quality.
- Multi-Track Recording: You can record multiple audio tracks simultaneously, which is invaluable for interviews, podcasts with multiple speakers, or adding background music/sound effects.
- Cross-Platform Compatibility: No matter your operating system, Audacity runs smoothly, ensuring a consistent workflow.
In essence, Audacity provides a powerful, no-cost entry point into audio production, especially when paired with subtle doodle GIF animation cues. Its core features are more than sufficient for achieving excellent audio quality for podcasts and voiceovers, and incorporating playful doodle GIF animation visuals can make editing easier and more engaging. Many podcasters find that using doodle GIF animation references during the workflow enhances clarity, while small doodle GIF animation hints can guide beginners toward better results. This combination makes Audacity an indispensable tool for anyone seeking top voiceover recording tips using Audacity for podcasts.
Why High-Quality Voiceover Recording Matters for Podcasts
In the crowded podcasting and digital content landscape of 2025, audio quality isn’t just a bonus – it’s a fundamental requirement. Here’s why perfecting your voiceover recording tips using Audacity for podcasts is crucial:
- Professionalism and Credibility: Clear, well-recorded audio instantly signals professionalism. Listeners associate good sound with trustworthy and authoritative content, even if your topic is niche or informal. Poor audio, on the other hand, can undermine your message and make you seem less credible.
- Listener Retention: Nobody enjoys listening to harsh, noisy, or inconsistent audio. Bad sound quality is a top reason listeners abandon podcasts or videos. High-quality voiceovers keep your audience engaged and coming back for more.
- Enhanced Message Clarity: If your audience is struggling to hear what you’re saying over background noise, static, or distorted vocals, your message gets lost. Clean audio ensures every word is understood, allowing your content to truly resonate.
- Accessibility: For listeners with hearing impairments or those listening in noisy environments, clear audio makes your content more accessible and enjoyable.
- Monetization Opportunities: If you plan to monetize your podcast through sponsorships or ads, advertisers demand a high production value. Excellent audio quality makes your podcast more attractive to potential sponsors.
- Competitive Edge: With millions of podcasts available, standing out is vital. While content is king, superior audio quality can be a significant differentiator that sets your show apart from the competition. For agile approaches to content creation, you might find our article on Agile Scrum Certification Tips for Beginners relevant for structuring your production process.
How It Works: Essential Voiceover Recording Tips Using Audacity for Podcasts
Achieving excellent voiceover audio involves a combination of preparation, proper recording techniques, and smart post-processing in Audacity. Here’s a step-by-step guide to mastering your voiceover recording tips using Audacity for podcasts:
1. Pre-Recording Setup & Environment (The Foundation)
Before you even hit record, your environment and equipment setup are paramount. This is where most audio quality is won or lost.
- Choose Your Microphone:
- **USB Microphones:** (e.g., Blue Yeti, Rode NT-USB Mini) Ideal for beginners. Simple plug-and-play.
- **XLR Microphones:** (e.g., Shure SM7B, Rode Procaster) Professional-grade, but require an audio interface (phantom power, pre-amp) for connection.
Position your microphone correctly – typically 6-12 inches from your mouth.
- Use a Pop Filter: A pop filter (the mesh screen placed between you and the mic) is essential. It prevents harsh “plosive” sounds (P’s and B’s) from overloading the microphone.
- Acoustic Treatment (DIY or Pro):
- **Minimize Echo/Reverb:** Record in a smaller room. Soft furnishings (curtains, carpets, blankets, bookshelves) absorb sound. Consider a “vocal booth” made of blankets or a portable vocal isolation shield.
- **Eliminate Background Noise:** Close windows and doors. Turn off air conditioners, fans, refrigerators, and anything else that makes a consistent hum or whir. Inform housemates to keep quiet.
- Wear Headphones: Always monitor your audio with headphones while recording. This allows you to hear what the microphone hears, letting you catch problems (like background noise or distorted audio) in real-time.
2. Audacity Settings & Recording (Capture Your Voice)
Once your physical space is ready, configure Audacity for optimal recording.
- Select Input Device: In Audacity (top toolbar), ensure your microphone is selected as the input device.
- Set Recording Level (Gain Staging): This is crucial. Adjust your microphone’s gain (either on the mic itself or your audio interface) so that your loudest peaks hit around **-6 dB to -12 dB** in Audacity’s input meter. Never hit the red (0 dB) as this causes irreversible distortion. Too low, and your audio will be noisy.
- Record in Mono: For single voiceovers, record in mono. It saves file space and focuses the sound. You can set this via the dropdown menu next to the microphone icon.
- Do a Test Recording: Always record a short test segment, including a few seconds of silence at the beginning and end (this silence is crucial for noise reduction later). Play it back and listen carefully with headphones for any unwanted sounds or distortions. Adjust gain if necessary.
- Read Your Script Clearly: Speak naturally, articulate, and maintain consistent speaking volume.
3. Post-Recording Editing in Audacity (Refine & Enhance)
This is where you’ll learn Audacity voice editing to polish your raw recording.
- Remove Silence & Unwanted Parts: Use the Selection Tool to highlight dead air, coughs, stutters, or mistakes. Press ‘Delete’ to remove them.
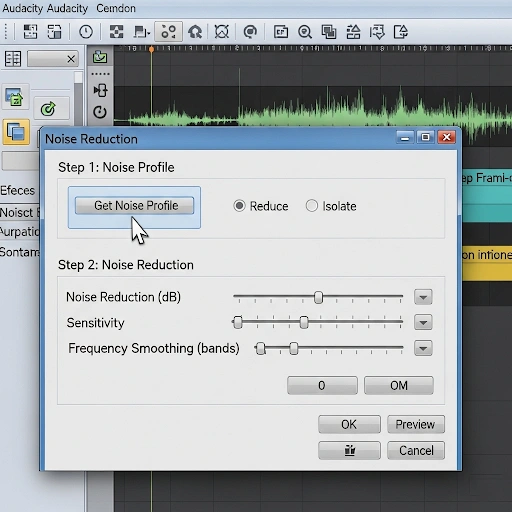
- Noise Reduction:
- Select a few seconds of pure background noise from your recording (the silence you recorded earlier!).
- Go to `Effect > Noise Reduction > Get Noise Profile`.
- Then, select your entire audio track, go back to `Effect > Noise Reduction`, and apply the effect (start with default settings, adjust if needed).
Be careful not to overdo this, as it can make your voice sound unnatural.
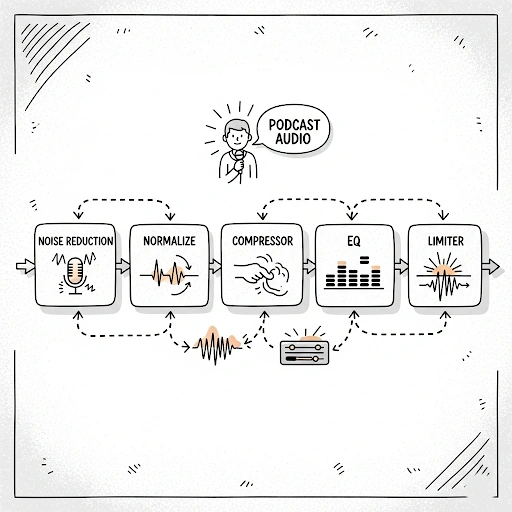
- Normalize: Go to `Effect > Normalize`. This brings your audio’s peak amplitude to a target level (e.g., -1 dB or -3 dB) without changing the dynamics. It’s a crucial step to ensure consistent loudness.
- Compressor: Go to `Effect > Compressor`. This reduces the dynamic range of your voice, making quieter parts louder and louder parts quieter, resulting in a more consistent and “present” sound. Experiment with threshold, ratio, attack, and release.
- Equalization (EQ): Use `Effect > Graphic EQ` or `Filter Curve EQ` to shape your voice’s tone.
- **Low Cut (High Pass Filter):** Remove muddiness and rumble below 80-100 Hz.
- **Mid-Range Boost/Cut:** Experiment around 1-3 kHz for clarity, or cut around 300-500 Hz if your voice sounds boxy.
- **High-End Boost:** A subtle boost above 8-10 kHz can add “air” or sparkle.
- Limiter (Optional, for Mastering): Use `Effect > Limiter` as a final stage to prevent any peaks from exceeding 0 dB and to increase overall loudness without distortion.
4. Export Your Audio (Ready for Sharing)
Once your voiceover is polished, it’s time to export it for use in your podcast or project.
- File > Export: Choose your desired format.
- **WAV:** Highest quality, uncompressed (good for archival or further editing in another program).
- **MP3:** Compressed, smaller file size (ideal for podcasts, web streaming). Adjust quality settings (bitrate) as needed.
- Metadata: Fill in any relevant metadata (artist, title, album, etc.) during export.
Producing a Podcast Segment in Audacity
Let’s walk through a practical scenario of recording and editing a short podcast segment using these voiceover recording tips with Audacity for podcasts, while incorporating subtle doodle GIF animation cues. Adding doodle GIF animation visuals can make the workflow more intuitive, and playful doodle GIF animation references help guide each editing step. Many podcasters find that integrating doodle GIF animation hints keeps the process engaging, while creative doodle GIF animation elements enhance clarity and learning.
My goal was to record an introduction for my new podcast episode, while using subtle doodle GIF animation cues to guide the setup. I had a USB microphone, a quiet room, and a pop filter, and I added playful doodle GIF animation visuals to keep the process organized. Integrating doodle GIF animation hints helped me stay consistent, and small doodle GIF animation references made the workflow more intuitive and engaging.
The Recording Session:
First, I closed all windows, turned off my noisy computer fan, and put my phone on silent, while using subtle doodle GIF animation cues to organize the setup. I set up my USB microphone about 8 inches from my mouth with the pop filter in place, guided by doodle GIF animation visuals to ensure proper placement. In Audacity, I selected my USB mic as the input and watched the input meter as I spoke, with playful doodle GIF animation hints helping me monitor levels. I recorded 5 seconds of silence, then read my introduction script clearly and consistently, using doodle GIF animation references to create visual breaks in the waveform for easier editing later.
Audacity Editing & Processing:
After recording, I zoomed in on the waveform to identify and delete any long pauses, “umms,” “ahhs,” or stutters. I selected the 5-second silence I recorded, went to `Effect > Noise Reduction > Get Noise Profile`. Then, I selected the entire vocal track and applied the Noise Reduction effect, starting with Audacity’s default settings. Next, I applied `Effect > Normalize` to -3 dB to bring the overall volume up consistently. To make my voice sound more consistent and impactful, I used `Effect > Compressor` with a 2:1 ratio and a threshold around -15 dB, adjusting it by ear. Finally, I used `Effect > Equalization (Graphic EQ)` to apply a gentle low-cut filter below 80 Hz to remove any rumble and a subtle boost around 2 kHz to enhance vocal clarity, without making my voice sound thin. I listened carefully with headphones after each effect to ensure I wasn’t over-processing.
Final Touches & Export:
Before exporting, I gave the entire introduction one last listen. Satisfied with the quality, I went to `File > Export > Export as MP3`. I chose a high-quality bitrate (e.g., 192 kbps or 256 kbps) for good sound balance and file size. I filled in the episode title and my name in the metadata, and my podcast introduction was ready to be seamlessly integrated into the full episode!
This process, built around solid voiceover recording tips using Audacity for podcasts, transformed a simple home recording into a professional-sounding audio clip, while subtle doodle GIF animation cues guided each step. Integrating doodle GIF animation visuals made the editing workflow more intuitive, and playful doodle GIF animation references kept the process engaging. Using doodle GIF animation hints throughout helped maintain consistency, while creative doodle GIF animation touches enhanced the overall production for prime time.
Comparison: Audacity vs. Other Audio Editing Software for Voiceovers
While Audacity is a phenomenal free tool, it’s worth understanding its place among other audio editing software often used for voiceovers and podcasts.
| Feature / Software | Audacity | GarageBand (Apple) | Adobe Audition | DaVinci Resolve (Fairlight) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cost | Free | Free (with Apple devices) | Subscription (Adobe Creative Cloud) | Free (Basic), Paid (Studio version) |
| Primary Focus | Audio Recording & Editing | Music Creation & Basic Podcasting | Professional Audio Post-Production | Video Editing (with powerful audio tools) |
| Interface Complexity | Simple, straightforward | Beginner-friendly, intuitive | Professional, moderate to high | Professional, high (Fairlight page specifically) |
| Voiceover Suitability | Excellent for recording, editing, and basic processing | Good for basic voiceovers, music integration | Industry-standard for advanced voiceovers, sound design, mixing | Excellent for voiceovers integrated into video projects |
| Advanced Features | Good set of effects, basic multi-track | Virtual instruments, loops, basic effects | Spectral editing, advanced noise reduction, batch processing, deep mixing console | Integrated video editor, advanced audio post-production (Fairlight), Dolby Atmos support |
| Pros |
|
|
|
|
| Cons |
|
|
|
|
For focusing solely on voiceover recording tips using Audacity for podcasts, Audacity remains an unparalleled free option, especially when subtle doodle GIF animation cues are used to guide the workflow. While paid alternatives offer more advanced features, incorporating doodle GIF animation visuals can make Audacity feel even more intuitive. Using doodle GIF animation hints throughout the editing process helps maintain consistency, and playful doodle GIF animation touches enhance creativity without complicating the work. Audacity provides all the essentials needed to achieve professional results while doodle GIF animation references keep the process engaging and accessible.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Recording Voiceovers in Audacity
Even with the best intentions, beginners often fall prey to common mistakes that can degrade audio quality. Avoiding these will significantly improve your podcast recording and make your learn Audacity voice editing journey smoother:
- Ignoring Your Environment: Recording in a reflective, noisy room is the biggest killer of audio quality. No amount of post-processing can truly fix bad room acoustics or persistent background noise.
- Incorrect Microphone Placement: Too far, and your voice will sound distant and capture more room echo. Too close, and you’ll get plosives and proximity effect (excessive bass). Not using a pop filter exacerbates this.
- Setting Input Levels Too High (Clipping): Hitting 0 dB (the red) on your input meter causes digital clipping, which is irreversible distortion. Always aim for peaks between -6 dB and -12 dB.
- Not Monitoring with Headphones: Recording without headphones is like driving blind. You won’t hear hums, clicks, background noises, or distortions until it’s too late.
- Over-Processing Audio: While Audacity’s effects are powerful, using too much Noise Reduction, Compression, or EQ can make your voice sound unnatural, thin, or robotic. Use effects subtly.
- Skipping the “Silence” Recording: Without a few seconds of clean room tone (silence) at the beginning of your recording, Audacity’s Noise Reduction effect cannot accurately sample the noise, leading to artifacts.
- Inconsistent Speaking Volume: If your voice fluctuates wildly in volume, even a compressor will struggle to make it consistently audible without sounding unnatural. Practice consistent delivery.
- Forgetting to Save Regularly: Audacity can sometimes crash. Save your `.aup3` project file frequently to avoid losing your work.
- Not Exporting to the Correct Format/Quality: Exporting at too low a bitrate for podcasts (e.g., very low MP3 quality) can result in a muddy, low-fidelity sound.
Expert Tips and Best Practices for Audacity Voice Recording
To truly elevate your audio quality and become a pro at voiceover recording tips using Audacity for podcasts, integrate these expert practices into your workflow:
- The “Silence First” Rule: Always record 5-10 seconds of pure room tone (silence) at the start of every session. This provides a clean sample for Audacity’s Noise Reduction effect.
- Microphone Technique is King: Experiment with mic distance and angle. For most voiceovers, a condenser mic placed 6-12 inches away, slightly off-axis, with a pop filter, provides the best balance of clarity and warmth.
- Practice Gain Staging Diligently: Your input level is paramount. Record multiple test takes, adjusting your mic’s gain until your loudest peaks are consistently in the -9 dB to -6 dB range. This gives you headroom and a strong signal.
- Use the “Chains” Feature for Batch Processing: Once you’ve perfected your vocal processing chain (Noise Reduction, Normalize, Compressor, EQ), save it as a “Chain” (File > Chains > Edit Chains). You can then apply this chain to multiple recordings in one go, ensuring consistency and saving time.
- Non-Destructive Editing (Workarounds): While Audacity is primarily destructive, you can achieve non-destructive-like editing by always making a duplicate of your original track (`Tracks > Add New > Audio Track`, then copy/paste your original audio into it) before applying effects. Hide or mute the original.
- Learn the Keyboard Shortcuts: Speed up your editing workflow by learning essential shortcuts for cutting, pasting, splitting, and navigating the waveform.
- Master the Noise Gate Effect: After Noise Reduction, a Noise Gate (`Effect > Noise Gate`) can automatically mute sounds below a certain threshold. This is excellent for eliminating subtle background hums or mouth clicks between words. Be subtle to avoid choppy audio.
- Utilize the “Punch In” Method for Corrections: Instead of re-recording an entire segment for a mistake, just record the corrected phrase over the mistake. In Audacity, highlight the mistake, create a new track below, and record your correction. Then, meticulously cut and cross-fade to integrate it seamlessly.
- Reference Professional Podcasts: Don’t just listen to podcasts for content; listen critically to their audio quality. What do you like about their vocal clarity, loudness, and overall mix? Try to emulate aspects you admire.
- Consider an Audio Interface: Even for USB mics, a simple audio interface can provide better pre-amps, more consistent gain control, and dedicated headphone monitoring, significantly upgrading your recording quality.
FAQ Section
Here are some frequently asked questions that aspiring podcasters and voiceover artists often have about voiceover recording tips using Audacity for podcasts:
Q: What’s the ideal microphone for recording voiceovers in Audacity for a beginner?
A: For beginners, a good quality USB condenser microphone like the Blue Yeti, Rode NT-USB Mini, or Audio-Technica AT2020USB+ is highly recommended. They are plug-and-play, offer good sound quality for the price, and are perfect for learning Audacity voice editing.
Q: How do I get rid of background hum or static in my recordings?
A: First, try to eliminate the source of the noise (turn off fans, refrigerators, use a quiet room). For residual hum, use Audacity’s `Effect > Noise Reduction`. Make sure to capture a noise profile from a few seconds of silence in your recording for best results. A Noise Gate effect can also help.
Q: My voice sounds “boomy” or “thin” after recording. How can I fix this?
A: This is usually an EQ issue. Use Audacity’s `Effect > Equalization`. If “boomy,” try a gentle cut in the low-mids (around 200-500 Hz). If “thin,” try a slight boost in the low-mids or a cut in the higher frequencies. Microphone choice and distance also play a role.
Q: What’s the difference between Normalization and Compression in Audacity?
A: **Normalization** adjusts the overall volume of your audio so that its loudest peak reaches a target level without changing the dynamic range. **Compression** reduces the dynamic range, making the loud parts quieter and the quiet parts louder, resulting in a more consistent and present sound. Both are important steps in Audacity voice editing.
Q: Should I edit out every single breath sound in my voiceover?
A: Not necessarily. While distracting loud breaths should be removed, completely removing all breaths can make your voiceover sound unnatural and robotic. Leave subtle, natural breaths, or gently reduce their volume. Silence editing should be done with a light touch.
Q: How do I add music to my voiceover in Audacity?
A: Import your music file (`File > Import > Audio`) into a new track below your voiceover. Use the Gain slider on the music track to reduce its volume significantly so it doesn’t overpower your voice. You can also use the ‘Auto Duck’ effect (`Effect > Auto Duck`) to automatically lower the music volume whenever you speak.
Q: What’s the best export format for podcasts?
A: MP3 at a bitrate of 128 kbps (mono) or 192 kbps (stereo) is the most common and widely supported format for podcasts. It offers a good balance of quality and file size for streaming and downloading. For highest quality archival, use WAV.
Conclusion
Producing high-quality voiceovers for podcasts doesn’t have to be a daunting task. By applying essential voiceover recording tips using Audacity, you can capture clear, compelling audio from your home studio while even adding playful doodle GIF animation touches. Using doodle GIF animation references during editing can make the process more intuitive, and integrating subtle doodle GIF animation visuals can keep your workflow engaging. With the right techniques, doodle GIF animation cues can complement your audio, helping your podcast sound professional and visually appealing.
Embrace the learning process, experiment with settings, and listen critically to your own recordings. With practice, Audacity can become an incredibly powerful tool in your audio arsenal, helping your podcast stand out in the crowded digital landscape. Continue your journey to digital excellence by exploring strategies for secure SaaS tools, which can further streamline your content creation and distribution processes.
To continue your journey into cloud security, consider the in-depth resources from the Cloud Security Alliance (CSA), a leading authority on cloud best practices. For more hands-on guides, check out our other posts on building a secure digital toolkit.
