Have an app idea but don’t know where to start? This guide breaks down the entire process, making modern app development accessible to everyone. Just like when you apply simple time management hacks to daily tasks, using time management hacks for beginners can ease the process, while effective time management hacks for productivity and practical time management hacks will help you stay consistent and focused on turning your app idea into reality.
Every day, you use apps that solve problems, entertain, and connect you to the world. Maybe you’ve thought, “I have a great idea for an app,” but felt blocked by the wall of code. In reality, that wall is lower than you think. Mobile development has changed, and with smart time management hacks, building apps is now more accessible. Using time management hacks for beginners, combined with productivity-focused time management hacks and simple daily time management hacks, this Kotlin guide helps creators, entrepreneurs, and beginners turn ideas into real apps.
- What is Kotlin and Why is it the Future of Android? A Guide with Time Management Hacks
- Why Learning Kotlin is a Game-Changer for You
- The 5 Core Steps to Building an Android App
- Let’s Build an App: A Simple Tip Calculator
- Kotlin vs. Java for Android Development
- Common Mistakes for Beginners to Avoid
- Expert Tips for Accelerating Your Learning
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Conclusion: You’re Ready to Build
What is Kotlin and Why is it the Future of Android? A Guide with Time Management Hacks
Kotlin is a modern programming language that boosts developer productivity. In 2019, Google made it the preferred choice for Android, moving away from Java. Much like smart time management hacks, Kotlin is safer, cleaner, and more enjoyable to use. It streamlines coding with fewer bugs, showing how effective time management hacks can cut waste, improve focus, and deliver faster results. With the right time management hacks, Kotlin empowers developers to build better apps more efficiently.
Think of it like upgrading from a manual typewriter to a modern word processor. Both can write a novel, but the word processor has spell check (safety), shortcuts (conciseness), and is just a more pleasant experience. In 2025, the trend is accelerating with Jetpack Compose, a modern UI toolkit built entirely with Kotlin. This makes it easier than ever to learn Kotlin app development because you’re learning the language and the modern way of building interfaces at the same time.

Why Learning Kotlin is a Game-Changer for You
Dedicating time to learn a new skill is always a big decision, and the right time management hacks make it easier to stay consistent. Learning Kotlin for Android development is like applying time-saving hacks that multiply your effort. With simple time management strategies, you can balance coding with other priorities. That’s why choosing Kotlin isn’t just smart—it mirrors the best time management hacks by offering a massive return on your investment.
Build a Career in a High-Demand Field
The demand for skilled mobile developers is not slowing down. Companies of all sizes need Android apps, and proficiency in Kotlin is one of the most sought-after skills in the job market. Mastering this skill can open doors to lucrative and fulfilling career opportunities in the tech industry.
Bring Your Own App Ideas to Life
This is the ultimate creative freedom. Whether you have an idea for the next big social network, a niche utility app for your hobby, or a tool to solve a problem in your community, knowing how to build it yourself is incredibly empowering. You are no longer just a consumer of technology; you become a creator.
Join a Modern, Supportive Developer Community
Kotlin developers are known for being passionate and supportive. Because the language is modern, the community is focused on best practices and helping newcomers succeed. There is a wealth of high-quality, up-to-date tutorials, forums, and open-source projects to learn from. This supportive ecosystem is just as important as the language itself, much like the communication skills needed in other fields, such as the negotiation techniques for professionals.
The 5 Core Steps to Building an Android App
The journey from idea to app follows a clear path. Here’s a high-level overview of the development workflow.
Step 1: Set Up Your Development Environment
Your digital workshop is an application called Android Studio. It’s the official Integrated Development Environment (IDE) for Android, built by Google. It’s a free, all-in-one package that includes a code editor, a UI designer, debugging tools, and an emulator to run your app on a virtual device.
Step 2: Understand the Project Structure
When you create a new project in Android Studio, it generates a set of files and folders. The two most important are the app/src/main/java folder, where your Kotlin code lives, and the app/src/main/res/layout folder, where you define your app’s user interface (UI).
Step 3: Design the User Interface (UI)
This is what the user sees and interacts with—buttons, text fields, images. The modern way to do this is with Jetpack Compose, which lets you build your UI directly in Kotlin code. The traditional method uses XML, a markup language, to define the layout, which you can then connect to your Kotlin code.
Step 4: Write the Logic with Kotlin
This is where the magic happens. You’ll write Kotlin code to handle user input (like a button click), perform calculations, save data, and update the UI. This is the “brain” of your application.
Step 5: Run and Debug Your App
With a single click, you can run your app on the Android Emulator or a physical Android device. Android Studio includes powerful debugging tools that help you find and fix errors (bugs) in your code, an essential part of the development process.
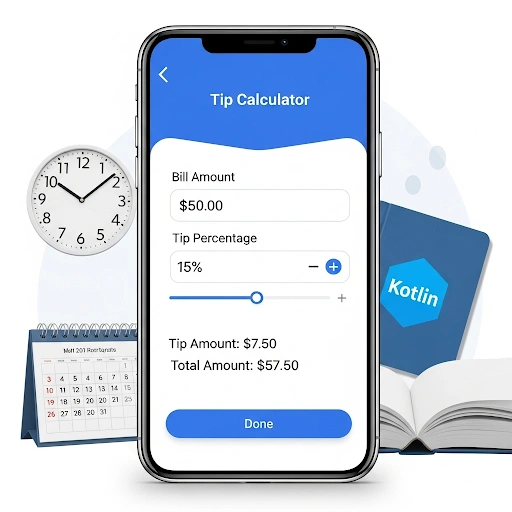
Let’s Build an App: A Simple Tip Calculator
Theory is great, but let’s make this concrete. We’ll build a very simple app that calculates a tip. The user enters a bill amount, and the app calculates a 15% tip and the total amount.
1. The User Interface (UI)
Using Jetpack Compose, the UI would be defined in Kotlin. We need three main elements: a text field for the bill amount, a button to trigger the calculation, and text elements to display the results.
2. The Kotlin Logic
When the “Calculate” button is clicked, we need to run some code. Here’s a simplified look at what that Kotlin code might look like. Don’t worry if it looks intimidating; the comments explain each step.
// This function runs when the button is clicked
fun calculateTip(billAmount: String) {
// Convert the text input (String) to a number (Double)
// Use ?.toDoubleOrNull() to avoid crashing if the input is not a valid number
val cost = billAmount.toDoubleOrNull()
// If the cost is null or zero, we can't calculate, so we stop here
if (cost == null || cost == 0.0) {
displayResult(0.0, 0.0) // Display zeros
return
}
// Calculate the tip (15%)
val tipAmount = cost * 0.15
// Calculate the total bill
val totalAmount = cost + tipAmount
// Call another function to update the text on the screen
displayResult(tipAmount, totalAmount)
}Kotlin vs. Java for Android Development
| Feature | Kotlin (Modern) | Java (Legacy) |
|---|---|---|
| Conciseness | Requires significantly less code to do the same task. | Often verbose, requiring more “boilerplate” code. |
| Null Safety | Built into the language, helping to eliminate the most common type of crash in Android apps. | Prone to NullPointerExceptions, a notorious source of bugs. |
| Modern Features | Supports modern programming paradigms like coroutines for easy asynchronous code. | Slower to adopt new language features. |
Common Mistakes for Beginners to Avoid
1. Trying to Learn Everything at Once
Android development is a vast field. Don’t try to master databases, networking, and animations all in your first week. Start with the basics: building simple UIs and handling user input. Master one concept before moving to the next.
2. Ignoring User Interface (UI) and User Experience (UX)
An app can have brilliant code, but if it’s ugly and confusing to use, no one will download it. Spend time looking at well-designed apps. Learn the basic principles of good design, like spacing, color, and intuitive navigation.
3. Not Using Version Control
Version control, primarily with a tool called Git, is like a “save” button for your entire project’s history. It allows you to track changes, revert to previous versions if something breaks, and collaborate with others. Start using it from day one, even for solo projects.
Expert Tips for Accelerating Your Learning
- Embrace Jetpack Compose: While many tutorials still use the older XML system, start with Jetpack Compose. It’s the future of Android UI, and learning it from the start will put you ahead of the curve.
- Learn to Read Documentation: The official Android Developer documentation is your best friend. Learning how to navigate it and find answers is a crucial skill for any developer.
- Build Projects, Not Just Follow Tutorials: Tutorials are great, but true learning happens when you try to build something on your own. Start with a small project you’re passionate about and work through the problems as they arise.
- Secure Your App’s Data: As you advance, you’ll handle user data. It’s vital to understand the basics of securing this information. Explore resources on topics like selecting secure tools for your backend to understand the principles involved.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Is Kotlin hard to learn for a complete beginner?
A: Kotlin is considered one of the more beginner-friendly languages due to its clean syntax. While any programming language has a learning curve, Kotlin’s is gentler than many alternatives.
Q: Can I build iOS apps with Kotlin?
A: Yes, through a technology called Kotlin Multiplatform. It allows you to share code (like business logic) between Android and iOS apps, but you’ll still need to build the UI for each platform separately. It’s an advanced topic but shows the power of the language.
Q: How do I make money with my app?
A: Common monetization strategies include charging a one-time fee for the app, offering in-app purchases for additional features, running ads, or using a subscription model.
