Step into the world of cybersecurity by learning to think like an attacker. This guide introduces the ethical hacking essentials that shape how professionals approach security. From basic tools to core concepts, these ethical hacking essentials help beginners understand real-world threats. By practicing ethical hacking essentials regularly, you’ll gain the confidence to analyze vulnerabilities and apply defensive strategies. Mastering these ethical hacking essentials is the first step toward building a strong foundation in cybersecurity.
The word “hacker” often brings to mind criminals in dark rooms, but ethical hacking shows another side. With ethical hacking essentials, you learn to spot and fix weaknesses before attackers exploit them. This guide introduces beginners to ethical hacking essentials, the core concepts, and the first toolkit to start safely. By mastering ethical hacking essentials step by step, you build skills that protect systems and data. Begin your journey into ethical hacking essentials and discover how to defend with the mindset of a white-hat hacker.
- What is Ethical Hacking (and What it Isn’t)?
- Why Learning to “Hack” is a Powerful Skill
- The Five Phases of an Ethical Hack
- Your First Hack: Using Nmap to Scan Your Own Network
- Your Essential Beginner’s Toolkit
- Common Mistakes for Beginners to Avoid
- Expert Tips for Your Learning Journey
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Conclusion: Your Journey into Cybersecurity Begins
What is Ethical Hacking (and What it Isn’t)?
Ethical hacking, or penetration testing, is the authorized practice of testing systems, networks, or apps to find weaknesses before attackers do. A core part of ethical hacking essentials is having clear permission from the system owner to perform these tests. Unlike malicious hacking, ethical hacking essentials focus on identifying risks and strengthening defenses, not stealing data. By learning ethical hacking essentials, beginners gain the mindset and skills to think like an attacker while staying within safe, legal boundaries. These ethical hacking essentials form the foundation for anyone starting in cybersecurity.
The Spectrum of Hackers: White, Black, and Grey Hats
To fully grasp the concept, it’s helpful to understand the different types of hackers, often categorized by the color of their “hat”:
- White-Hat Hackers: These are the good guys. They are security professionals who use their skills for defensive purposes. They have a strict code of ethics and always work with permission. Their work is crucial for securing the digital world.
- Black-Hat Hackers: These are the criminals. They hack into systems with malicious intent, whether for financial gain, espionage, or simply to cause chaos. Their actions are illegal and harmful.
- Grey-Hat Hackers: This group falls somewhere in between. A grey-hat hacker might look for vulnerabilities in a system without permission but will report them to the owner, sometimes requesting a fee. While their intent may not be malicious, their unauthorized actions are still legally and ethically ambiguous.
In 2025, as the world becomes more interconnected, the attack surface for cyber threats grows rapidly. From startups to global corporations, every organization is at risk. This is where ethical hacking essentials play a crucial role, giving defenders the tools to identify and mitigate vulnerabilities. The shift goes beyond simple scans toward adversary emulation, a practice rooted in ethical hacking essentials that mirrors real attacker behavior. Learning these ethical hacking essentials means mastering defensive offense, a vital skill in cybersecurity. With continuous practice, ethical hacking essentials prepare you to face evolving digital threats with confidence.
Why Learning to “Hack” is a Powerful Skill
Stepping into the mindset of an attacker offers a unique perspective with value far beyond cybersecurity. By exploring ethical hacking essentials, you begin to see how vulnerabilities are identified before they become real threats. This way of thinking, grounded in ethical hacking essentials, sharpens problem-solving skills and boosts digital awareness. Practicing ethical hacking essentials not only prepares you for a career in security but also builds resilience in navigating today’s connected world. Ultimately, ethical hacking essentials provide a foundation for understanding both risks and defenses in the digital age.
Unlock a High-Demand, High-Impact Career
The cybersecurity industry is facing a massive talent shortage. Companies are desperately seeking skilled professionals who can help them defend against ever-evolving threats. A career in ethical hacking is not only financially rewarding but also offers the satisfaction of playing a crucial role in protecting data, privacy, and critical infrastructure. Job titles include Penetration Tester, Security Analyst, Security Consultant, and Vulnerability Assessor, among others.
Think Critically and Solve Complex Problems
Ethical hacking is the ultimate problem-solving discipline. It teaches you to look at systems not just for what they are supposed to do, but for all the ways they can be made to fail. This analytical, out-of-the-box thinking is a valuable asset in any technical or strategic role. You learn to deconstruct complex systems, identify hidden assumptions, and chain together small, seemingly insignificant flaws to achieve a greater impact.
Become a Better Defender (and Developer)
You can’t defend against a threat you don’t understand. By learning the tools and techniques of attackers, you gain a profound understanding of how to build more secure systems from the ground up. This knowledge is invaluable for software developers, system administrators, and anyone involved in building or managing technology. This strategic thinking is a skill that translates across disciplines, much like the professional negotiation skills we’ve discussed previously.
The Five Phases of an Ethical Hack
A professional ethical hacking engagement follows a structured methodology. Understanding these five phases provides a framework for your learning and practice.
1. Reconnaissance (Information Gathering)
This is the planning phase. The hacker gathers as much information as possible about the target. This can be passive (like searching public records and social media) or active (like scanning the target’s network to see what’s open). The goal is to create a map of the target’s digital footprint. This includes finding IP address ranges, domain names, employee names and email formats, and technologies used by the company. Tools like Maltego and theHarvester are used for this phase.
2. Scanning
Using the information from reconnaissance, the hacker uses tools to actively scan the target’s systems for vulnerabilities. This involves looking for open ports, identifying the services running on those ports, and using vulnerability scanners to find known weaknesses. This phase can be broken down into three parts: port scanning (using Nmap to see what doors are open), vulnerability scanning (using tools like Nessus or OpenVAS to check for known flaws), and network mapping (visualizing the network architecture).
3. Gaining Access
This is the phase where the “hacking” happens. The attacker uses the vulnerabilities discovered during scanning to exploit the system and gain access. This could involve using an exploit against a software bug, cracking a weak password, or tricking an employee with a phishing email. This is often the most creative phase, requiring the hacker to leverage the information they’ve gathered to bypass security controls.
4. Maintaining Access
Once an attacker has a foothold, their goal is to maintain that access. They may install backdoors, create new user accounts, or escalate their privileges to gain more control over the system, allowing them to return later. This phase is about establishing persistence within the network, often by blending in with normal traffic to avoid detection.
5. Analysis and Reporting (Covering Tracks)
For a malicious hacker, this phase is about covering their tracks to avoid detection. For an ethical hacker, this is the most important phase. They analyze the vulnerabilities they found, document how they were exploited, and create a detailed report with recommendations for the organization to fix the issues. A good report includes an executive summary for management and a technical deep-dive for the IT team, with clear, actionable steps for remediation.

Your First Hack: Using Nmap to Scan Your Own Network
Let’s make this practical. One of the first and most fundamental tools you’ll use is Nmap (Network Mapper). It’s a free, open-source tool for network discovery and security auditing. We’ll use it to perform a basic scan on your own home network to see what devices are connected.
1. The Setup
- Disclaimer: Only ever run Nmap on networks you own or have explicit permission to scan. Unauthorized scanning is illegal.
- Installation: Download and install Nmap from the official website, nmap.org.
- Find Your Network Range: Open a command prompt (on Windows) or terminal (on Mac/Linux) and type
ipconfigorifconfigto find your local IP address and subnet mask. It will likely be something like192.168.1.X.
2. The Scan
Now, run a simple “ping scan” to discover all the active devices on your network. If your network is 192.168.1.0/24, the command would be:
nmap -sn 192.168.1.0/243. Analyzing the Results
Nmap will return a list of IP addresses that are currently “up” on your network. You might be surprised by what you find! You’ll see your computer, your phone, your router, and maybe smart TVs, game consoles, or other IoT devices. This is the first step of reconnaissance—mapping the digital environment.
Your Essential Beginner’s Toolkit
| Tool / Category | What It Is | Why It’s Essential |
|---|---|---|
| Kali Linux | A Linux distribution pre-loaded with hundreds of security tools. | Provides a complete, ready-to-use hacking lab in a safe, isolated environment (a virtual machine). |
| Nmap | A powerful network scanner for discovering hosts and services. | The first step in understanding any target network. It’s the “eyes” of a hacker. |
| Burp Suite | A web application security testing tool. | Allows you to intercept, inspect, and modify traffic between your browser and a web server to find vulnerabilities. |
| Metasploit | A framework for developing and executing exploit code against a remote target. | Helps you understand and test the “Gaining Access” phase by safely using real-world exploits. |
| Wireshark | A network protocol analyzer. | Lets you capture and inspect the data traveling on your network at a low level, essential for deep analysis and troubleshooting. |
| John the Ripper | A password cracking tool. | Used to test the strength of passwords by attempting to crack hashed password files obtained from a system. |
Common Mistakes for Beginners to Avoid
1. Hacking Without Permission
This is the golden rule. The difference between an ethical hacker and a criminal is permission. Never test systems you do not own or have explicit, written authorization to test. The consequences are severe.
2. Getting Lost in the Tools
It’s tempting to learn a hundred different tools, but it’s more important to understand the underlying concepts. A tool is only as good as the person using it. Focus on learning networking, operating systems, and web technologies first.
3. Ignoring the Scope of an Engagement
In a professional setting, you’ll be given a “scope”—a clear definition of what you are and are not allowed to test. Going outside this scope, even accidentally, can have serious legal and professional consequences.
4. Poor or Non-Existent Reporting
Finding a vulnerability is only half the job. If you can’t clearly and concisely explain the flaw, its potential impact, and a recommended fix to the client, your work has little value. Good communication and report-writing skills are just as important as technical skills.
Expert Tips for Your Learning Journey
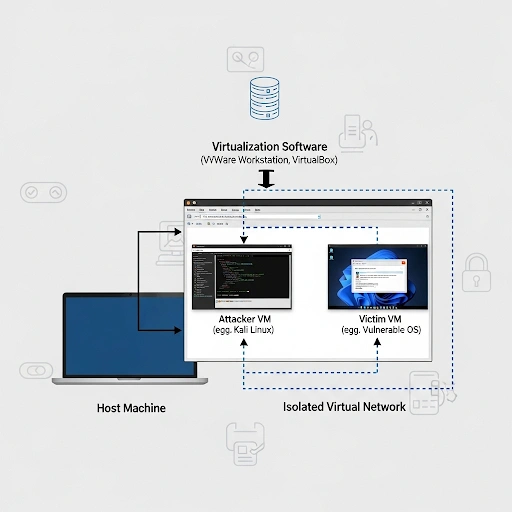
- Build a Home Lab: The safest way to practice is in your own controlled environment. Use virtualization software like VirtualBox or VMware to set up virtual machines. You can install Kali Linux as your “attacker” machine and download intentionally vulnerable applications (like Metasploitable or DVWA) as your “target.”
- Focus on the Fundamentals: Before you can break things, you need to know how they work. Spend time learning the basics of TCP/IP networking, the Linux command line, and how web applications function (HTTP, HTML, JavaScript).
- Join a Community: The cybersecurity community is vast and supportive. Participate in online forums, go to local meetups (like DEF CON groups), and engage in Capture The Flag (CTF) competitions on platforms like Hack The Box or TryHackMe.
- Document Everything: Get into the habit of taking detailed notes as you learn and practice. This is a critical skill for the reporting phase of an ethical hack. For more on the importance of clear documentation and security, you can explore resources on selecting secure tools.
- Learn a Scripting Language (Python): Python is the Swiss Army knife of the cybersecurity world. It can be used to automate repetitive tasks, create custom tools, and parse large amounts of data. Learning basic Python scripting will significantly enhance your effectiveness.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Do I need to be a programmer to be an ethical hacker?
A: While you don’t need to be an expert developer, a basic understanding of scripting languages (like Python or Bash) is extremely helpful for automating tasks and understanding exploits. You don’t need to build apps, but you should be able to read and understand code.
Q: What certifications are good for beginners?
A: For absolute beginners, the CompTIA Security+ provides a strong foundational knowledge of security concepts. The next step for aspiring ethical hackers is often the Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH) or the more hands-on Offensive Security Certified Professional (OSCP).
Q: Is ethical hacking legal?
A: Yes, it is 100% legal, provided you have explicit, written permission from the owner of the systems you are testing. Without permission, it is a crime.
Q: How much can an ethical hacker earn?
A: Salaries vary widely based on experience, location, and certifications, but it is a well-compensated field. Entry-level positions can start around $60,000-$80,000 USD, with senior penetration testers earning well into the six figures.
Q: What is the difference between a vulnerability assessment and a penetration test?
A: A vulnerability assessment is typically an automated scan that identifies potential weaknesses and produces a report. A penetration test is a more in-depth, hands-on process where a hacker actively tries to exploit those vulnerabilities to see how far they can get, simulating a real-world attack.
