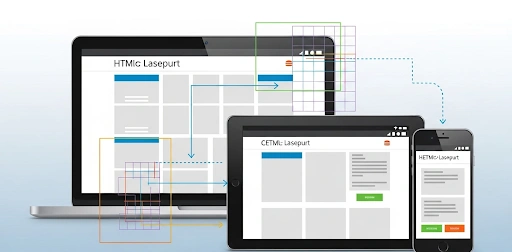
In today’s multi-device world, people access websites on everything from tiny smartphone screens to large desktop monitors. If your website isn’t designed to adapt seamlessly to these different screen sizes, you’re losing visitors, frustrating users, and potentially harming your search engine rankings. This is where responsive web design comes in, ensuring your content looks and functions beautifully on any device. For aspiring web developers, mastering this skill is non-negotiable. This comprehensive HTML CSS responsive design tutorial beginners need is your gateway to building modern, adaptive websites.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through the fundamental concepts and practical techniques of responsive web design using HTML and CSS. We’ll cover essential topics like meta viewport, fluid grids, flexible images, and, most importantly, media queries. Our aim is to help you HTML CSS responsive design specifically tailored for responsiveness, equipping you with the skills to create websites that provide an optimal viewing experience for every user, on every device.
- What is Responsive Web Design?
- Why Responsive Design Matters: Benefits for Your Website
- Core Techniques: How to Implement Responsive Design
- Real-Life Use Case: Building a Responsive Blog for Beginners
- Comparison: Responsive Design vs. Separate Mobile Sites
- Common Mistakes in Responsive Web Design for Beginners
- Expert Tips and Best Practices for HTML CSS Responsive Design Tutorial Beginners
- FAQ Section
- Q: What is the most important tag for responsive design?
- Q: Can I use responsive design with older HTML/CSS versions?
- Q: What are common breakpoints for responsive design?
- Q: Is responsive design hard to learn web design basics?
- Q: What is the “mobile-first” approach?
- Q: Can I use CSS frameworks like Tailwind CSS for responsive design?
- Q: How does responsive design affect website loading speed?
- Conclusion
What is Responsive Web Design?
Responsive web design (RWD) is an approach to HTML CSS responsive design that makes web pages render well on a variety of devices and screen sizes. Instead of creating separate websites for desktop, tablet, and mobile, responsive design with HTML and CSS uses flexible layouts, fluid images, and media queries to adapt the website’s appearance and functionality to the user’s screen. This means one well-structured HTML CSS responsive design can serve many devices, ensuring a consistent and optimal user experience across the board while keeping maintenance efficient.
The core principles of responsive design include:
- **Fluid Grids:** Using relative units (percentages, `em`, `rem`, `vw`, `vh`) instead of fixed pixel widths for layout elements.
- **Flexible Images and Media:** Ensuring images and videos scale proportionally within their containers.
- **Media Queries:** CSS rules that apply styles based on device characteristics like screen width, height, or orientation.
- **Mobile-First Approach:** Designing for the smallest screen first, then progressively enhancing for larger screens.
Mastering these concepts is crucial for anyone following an HTML CSS responsive design tutorial beginners should understand.

Why Responsive Design Matters: Benefits for Your Website
Implementing responsive web design offers significant advantages for your website and its users.
Improved User Experience (UX)
Users expect websites to look good and be easy to navigate on any device. A responsive design eliminates the need for pinching, zooming, or excessive scrolling on mobile, providing a seamless and enjoyable experience. This directly translates to higher user satisfaction and engagement.
Enhanced SEO (Search Engine Optimization)
Google prioritizes mobile-friendly websites in its search rankings. A responsive design is Google’s recommended approach for mobile optimization, which can lead to better visibility in search results, especially for mobile searches. This makes responsive design a critical component of modern SEO strategies.
Cost-Effectiveness and Easier Maintenance
Instead of building and maintaining separate websites for different devices, responsive design allows you to manage a single codebase. This significantly reduces development time, maintenance costs, and content management efforts. It’s a more efficient approach for long-term website management. This is a key reason to learn web design basics with responsiveness in mind.
Future-Proofing Your Website
With new devices and screen sizes constantly emerging, a responsive design ensures your website remains adaptable to future technologies without requiring a complete redesign. It provides a flexible foundation that can scale and adjust as the digital landscape evolves. For foundational HTML and CSS knowledge, check out our guide on HTML CSS Basics for Beginners.
Core Techniques: How to Implement Responsive Design
Mastering responsive design involves understanding and applying these fundamental HTML and CSS techniques. This section serves as a practical HTML CSS responsive design tutorial beginners can follow.
1. The Viewport Meta Tag (HTML)
This is the absolute first step for responsive design. Add this meta tag in the “ section of your HTML document:
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
This tag tells the browser to set the viewport width to the device’s width and the initial zoom level to 1.0. Without it, mobile browsers might render your page at a desktop width, making it tiny and unreadable.
2. Fluid Grids (CSS)
Instead of fixed pixel widths, use relative units for your layout elements.
- **Percentages (`%`):** For column widths, `width: 50%;` makes an element take up half the parent’s width.
- **`em` and `rem`:** For font sizes and spacing. `em` is relative to the parent element’s font size, `rem` is relative to the root (`html`) font size.
- **`vw` and `vh`:** Viewport width and viewport height. `1vw` is 1% of the viewport width. Useful for elements that should scale with the screen.
- **`max-width`:** Use `max-width: 100%;` for images to ensure they don’t overflow their containers on smaller screens.
This ensures your layout adapts fluidly as the screen size changes, a core concept in any HTML CSS responsive design tutorial beginners follow.
3. Flexible Images and Media (CSS)
To prevent images and videos from breaking your layout on smaller screens, apply simple CSS rules:
img, video {
max-width: 100%;
height: auto; /* Maintains aspect ratio */
display: block; /* Removes extra space below images */
}
This ensures media scales down to fit its container without overflowing.
4. Media Queries (CSS)
Media queries are the backbone of responsive design, allowing you to apply different CSS rules based on screen characteristics. They are essential for adapting layouts and styles at specific “breakpoints.”
/* Styles for screens smaller than 768px (e.g., mobile) */
@media (max-width: 767px) {
.container {
width: 95%;
padding: 1rem;
}
.column {
width: 100%; /* Columns stack on mobile */
float: none;
}
}
/* Styles for screens between 768px and 1024px (e.g., tablet) */
@media (min-width: 768px) and (max-width: 1023px) {
.column {
width: 50%; /* Two columns on tablet */
}
}
/* Styles for screens 1024px and wider (e.g., desktop) */
@media (min-width: 1024px) {
.column {
width: 33.33%; /* Three columns on desktop */
}
}
This example shows how to change column layouts based on screen width, a fundamental technique to learn web design basics for responsiveness. More details on media queries can be found on W3Schools.

Real-Life Use Case: Building a Responsive Blog for Beginners
Consider Alex, a beginner web developer building his first personal blog. He wants to ensure his blog looks great on both his laptop and his smartphone. He followed an HTML CSS responsive design tutorial beginners could easily grasp.
**Alex’s Responsive Blog Implementation:**
- He started by adding the viewport meta tag to his HTML.
- He used percentages for his main content area and sidebar widths. For example, `main { width: 70%; float: left; }` and `aside { width: 30%; float: left; }`.
- He applied `max-width: 100%;` to all his images to ensure they scaled down on smaller screens.
- He then used a media query: `@media (max-width: 767px) { main, aside { width: 100%; float: none; } }`. This made his sidebar stack below the main content on mobile, creating a single-column layout.
- He tested his blog on various devices and used his browser’s developer tools to simulate different screen sizes, refining his CSS as needed.
**The Result:** Alex’s blog now provides an excellent user experience on any device. Visitors can easily read his articles, browse his categories, and view images without frustration, demonstrating his ability to HTML CSS responsive design for responsive development.
Comparison: Responsive Design vs. Separate Mobile Sites
Before responsive design, creating separate mobile versions of websites was common. Here’s why responsive design is superior, especially for beginners learning to learn web design basics:
| Aspect | Responsive Web Design | Separate Mobile Site (e.g., m.example.com) |
|---|---|---|
| Codebase | Single codebase for all devices. | Separate codebases for desktop and mobile. |
| Maintenance | Easier (update once, applies everywhere). | More complex (update two sites). |
| SEO Impact | Google-recommended, better mobile ranking. | Can lead to duplicate content issues, SEO challenges. |
| Adaptability to New Devices | Highly adaptable to new screen sizes. | Requires new site versions for new device categories. |
| User Experience | Seamless experience across all devices. | Can lead to redirects, inconsistent features. |
For modern web development, responsive design is the clear winner, offering superior flexibility, maintainability, and user experience, making it a crucial skill from any HTML CSS responsive design tutorial beginners use.
Common Mistakes in Responsive Web Design for Beginners
Even with clear instructions, beginners can make mistakes. Avoid these common pitfalls:
- Forgetting the Viewport Meta Tag: Without this, your mobile site won’t render correctly, no matter how good your CSS is.
- Using Fixed Pixel Widths: Relying on `width: 960px;` instead of `max-width: 100%;` or percentages will break your layout on smaller screens.
- Too Many Breakpoints: Creating a media query for every possible device size. Focus on major content shifts (e.g., mobile, tablet, desktop) rather than specific device widths.
- Ignoring Mobile-First: Trying to adapt a complex desktop design to mobile. It’s often easier to build for mobile first and then expand for larger screens.
- Not Testing Enough: Only testing on your own phone. Use browser developer tools to simulate various screen sizes and orientations.
- Over-Complicating Media Queries: Writing overly complex or nested media queries. Keep them clean and focused on specific layout adjustments.
Expert Tips and Best Practices for HTML CSS Responsive Design Tutorial Beginners
To truly master responsive web design, integrate these expert tips into your learning and practice:
1. Start with Mobile-First Design
Always design and code for the smallest screen first. This forces you to prioritize content and functionality, making it easier to progressively enhance the design for larger screens. This is a fundamental concept in any effective HTML CSS responsive design tutorial beginners should follow.
2. Use Relative Units Consistently
Embrace percentages, `em`, `rem`, `vw`, and `vh` for widths, heights, margins, and padding. This ensures your layout scales proportionally across different screen sizes, providing inherent responsiveness. Avoid fixed pixel values for layout elements wherever possible.
3. Choose Breakpoints Based on Content, Not Devices
Instead of targeting specific device widths (e.g., iPhone 12 Pro), let your content dictate your breakpoints. When your layout starts to look awkward or break at a certain screen size, that’s your cue to add a media query and adjust the design. This makes your design more robust and future-proof.
4. Test on Real Devices and Browser Developer Tools
While browser developer tools (e.g., Chrome DevTools’ Device Mode) are excellent for simulation, always test your responsive designs on actual smartphones and tablets. This helps catch subtle rendering issues or touch interaction problems. Consistent testing is vital to truly HTML CSS responsive design for responsiveness.
5. Prioritize Performance
Responsive design should not come at the cost of performance, especially on mobile. Optimize images, minimize CSS and JavaScript, and consider lazy loading. A fast-loading responsive site provides a superior user experience and better SEO. This is a key aspect of any comprehensive HTML CSS responsive design tutorial beginners should master.

FAQ Section
Q: What is the most important tag for responsive design?
A: The “ tag in the “ section of your HTML is the most crucial. It tells the browser to correctly scale your page to the device’s width, which is the foundation of responsive behavior for any HTML CSS responsive design tutorial beginners follow.
Q: Can I use responsive design with older HTML/CSS versions?
A: Responsive design primarily relies on CSS3 features (like media queries) and modern HTML CSS responsive design. While you can apply some responsive principles to older code, it’s best learned and implemented with modern HTML5 and CSS3 for full functionality, as taught in any good HTML CSS responsive design tutorial beginners should use.
Q: What are common breakpoints for responsive design?
A: Common breakpoints often target typical device categories:
- **Small (Mobile):** `max-width: 575px`
- **Medium (Tablet):** `min-width: 576px` and `max-width: 991px`
- **Large (Desktop):** `min-width: 992px`
However, it’s best to let your content dictate your specific breakpoints, as emphasized in this HTML CSS responsive design tutorial beginners guide.
Q: Is responsive design hard to learn web design basics?
A: Responsive design builds upon basic HTML and CSS. While it adds a layer of complexity with media queries and fluid layouts, it’s entirely learnable for beginners. This HTML CSS responsive design tutorial beginners guide breaks it down into manageable steps. Consistent practice is key.
Q: What is the “mobile-first” approach?
A: Mobile-first is a design philosophy where you start designing and coding for the smallest screen (mobile) first, and then progressively add styles for larger screens using `min-width` media queries. This ensures a solid foundation for mobile users and often leads to cleaner, more efficient code. It’s a best practice taught in any good HTML CSS responsive design tutorial beginners should use.
Q: Can I use CSS frameworks like Tailwind CSS for responsive design?
A: Yes, absolutely! Frameworks like Tailwind CSS, Bootstrap, or Foundation are built with responsive design principles in mind and provide utility classes and components that make building responsive layouts much faster and easier. They abstract away much of the direct media query writing, helping you to HTML CSS responsive design more quickly.
Q: How does responsive design affect website loading speed?
A: A well-implemented responsive design can improve loading speed on mobile by serving optimized images and resources relevant to the device. However, a poorly implemented one (e.g., sending large desktop images to mobile) can slow it down. Optimizing images and code is crucial for performance, a key tip in any HTML CSS responsive design tutorial beginners should follow.
Conclusion
Mastering HTML and CSS responsive design is an essential skill for any aspiring web developer in today’s multi-device world. By understanding the viewport meta tag, embracing fluid grids and flexible media, and effectively utilizing media queries, you can create websites that adapt beautifully to any screen size. This HTML CSS responsive design tutorial beginners guide provides the foundational knowledge you need.
To continue your journey into cloud security, consider the in-depth resources from the Cloud Security Alliance (CSA), a leading authority on cloud best practices. For more hands-on guides, check out our other posts on building a secure digital toolkit.